- Blog
- 07.12.2022
- Dev Dialogues
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) in the Cloud: IAM Roles & Matillion

Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security authorization model that can be applied in Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform.
Being cloud-native, Matillion integrates fully into each cloud provider’s own RBAC implementation. That means Matillion fits naturally into an enterprise-wide cloud security strategy.
This article will describe how best to take advantage of RBAC with Matillion.
Prerequisites for Cloud Access Control
The prerequisites for configuring RBAC with Matillion are:
- Access to Matillion ETL or Matillion Data Loader
- Access to the RBAC or IAM area in the cloud console(s) you intend to use
- It will help if you know which cloud services you intend to use with Matillion, and what levels of access. The only mandatory service is storage, but Matillion can interface with many others
What is RBAC?
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) means that access to resources – such as cloud storage – is governed by membership of roles.
- Roles can be granted privileges on cloud resources. For example: “allowed to read from this area in cloud storage,” or “allowed to send messages to this queue”
- Identities can be members of Roles

Configuring RBAC is known as Identity and Access Management (IAM).
What is IAM?
Identity Access Management (IAM) concerns the details of how RBAC is implemented.
Inside a cloud provider console, IAM involves the management of Roles, and the assignment of Privileges and Identities. In other words, IAM is the toolset that enables you to put in place essential preventive controls that help block security incidents from happening.
With Matillion there are two main ways to use RBAC Identities:
- Identity confirmed by the cloud provider – for example, if you are running your own Matillion ETL instance as a virtual machine. This is known as Instance Credentials.
- Identity confirmed by owning a secret – for example, when setting up Cloud Credentials in Matillion Data Loader, or User Defined Credentials in Matillion ETL
If you have a choice of both options, instance credentials are generally simpler to manage than secrets.
 If you have a choice of using either Instance Credentials or a Secret, use Instance Credentials as a first preference
If you have a choice of using either Instance Credentials or a Secret, use Instance Credentials as a first preference
IAM implementation methods vary significantly between cloud platform providers. Different kinds of privileges can be granted, and different kinds of Identities exist.
IAM in AWS
Roles and Identities are managed in the IAM area of the AWS cloud console, using Role, Policy, and User objects. Many fine-grained privileges exist, all categorized broadly as reading, writing, or administration.
Privileges can be granted either through a named Policy, or attached inline directly. Using named Policies generally makes IAM easier to administer.

Grant privileges using Policy objects in preference to inline
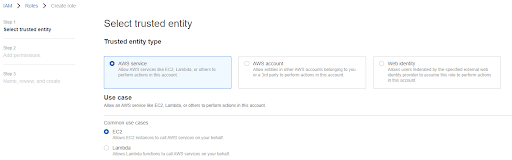
To use Instance Credentials with an EC2 instance, first create an IAM Role with Trusted Entity type of EC2. This is referred to as a Service Role. Grant the minimum set of privileges for the cloud services you intend to use with Matillion.
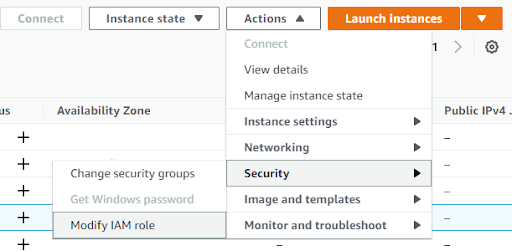
To attach the Service Role to an EC2 instance, follow “Modify IAM Role” from the Security menu under Actions.
Once a Service Role has been attached to an EC2 instance, it is known as an Instance Profile.
 To use Instance Credentials with Matillion in AWS, create a Service Role Identity, with the minimum set of privileges, and assign the Service Role to your virtual machine
To use Instance Credentials with Matillion in AWS, create a Service Role Identity, with the minimum set of privileges, and assign the Service Role to your virtual machine
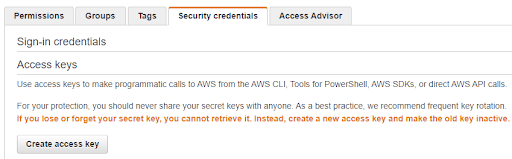
To use a Secret rather than Instance Credentials, grant the minimum set of privileges to an IAM User rather than to a Service Role.
Secret credentials are created in the IAM user management page. Create a Key and a Secret Key by following “Create Access Key”.
IAM in Azure
Within Azure, Roles and Identities are managed by a cloud hosted version of Active Directory, known as a “tenant” or a “directory.” There are many fine-grained privileges, grouped broadly as:
- Owner – The most powerful administrator privilege
- Contributor – Full access, but without user administration privileges
- Reader – Read-only access
- Service-specific privileges
To use Instance Credentials, start by creating a Managed Identity. Grant the minimum set of privileges for the cloud services you intend to use with Matillion. To attach it to a virtual machine, first switch off the system-assigned identity in the Identity Settings panel:
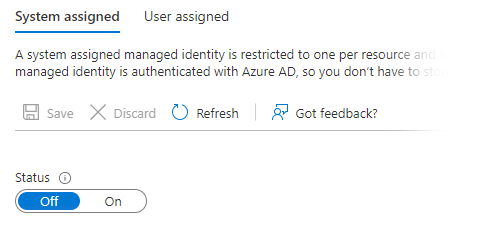
Then add the Managed Identity in the User Assigned settings.
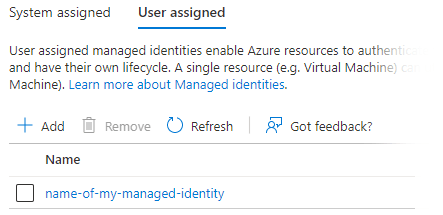
 To use Instance Credentials with Matillion in Azure, create a Managed Identity with the minimum set of privileges, and assign the Managed Identity to your virtual machine
To use Instance Credentials with Matillion in Azure, create a Managed Identity with the minimum set of privileges, and assign the Managed Identity to your virtual machine
To use a Secret rather than Instance Credentials in Azure means creating an App Registration. This is an external-facing authentication mechanism that delegates to Azure Active Directory. Grant the minimum set of privileges to an App Registration rather than to a Managed Identity.
Secret credentials are created in the App Registration management page
- Tenant ID and Client ID are in the overview
- Go to the Certificates & Secrets panel, press “New client secret” and copy the value of the client secret that is created

 To avoid a “Blob Storage: Check Credentials” error when testing, you must grant access to at least one Storage Account – such as Storage Blob Data Reader
To avoid a “Blob Storage: Check Credentials” error when testing, you must grant access to at least one Storage Account – such as Storage Blob Data Reader
IAM in GCP
For application workloads such as Matillion, GCP uses identities known as Service Accounts. Permissions are granted through Roles. You can create custom Roles, or you can take advantage of predefined Roles with fine-grained controlled access to specific resources.
To use Instance Credentials, start by creating a Service Account. Grant the minimum set of Roles for the cloud services you intend to use with Matillion. To attach it to a virtual machine, choose a Service Account while creating or editing a Compute Engine virtual machine.


To use Instance Credentials with Matillion in GCP, create a User Defined Service Account with the minimum set of privileges, and assign it to your virtual machine
To use a Secret rather than Instance Credentials in GCP, start with a Service Account, and follow the Add Key button under the Keys menu.
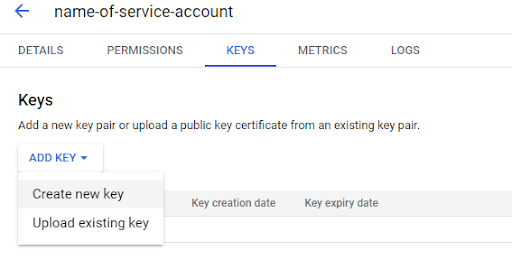
Choose JSON format, and download the secret credentials as a file.
Using IAM roles in Matillion
From Matillion ETL, you can use either:
- Instance Credentials – by selecting “Instance Credentials” in the Environment editor
- Identity confirmed by owning a secret, by creating a User Defined Credentials object from the Project menu and selecting it in the Environment editor
From Matillion Data Loader, you can use:
- Identity confirmed by owning a secret, by using the Manage cloud credentials dialog
Next Steps
Set up RBAC with Matillion!
Verify your level of access by developing workflows in Matillion ETL.
Read the cloud provider reference documentation:
- Understanding RBAC in AWS
- Understanding RBAC in Azure
- Understanding RBAC in GCP
Read the Matillion cloud credential reference documentation
Learn more about security on Matillion Academy
Want to learn more about security controls and permissions within Matillion? Take the Matillion Security course on Matillion Academy. The course is a comprehensive look at all of the aspects of security for enterprises using Matillion.
Featured Resources
Custom Connector for Public Statistics (Police API)
A demonstration of the practical steps for setting up components, manipulating and validating data, creating and scheduling ...
BlogMastering Git At Matillion. An In-Depth Guide To Merging
Merging in Git is the process of integrating changes from one branch into another. Merging is the backbone of collaboration in ...
BlogWhat is an API?
What is an API? An API is an application programming interface that is a way for two or more computer programs or components ...
Share: